Arrhythmias
Understanding Arrhythmias
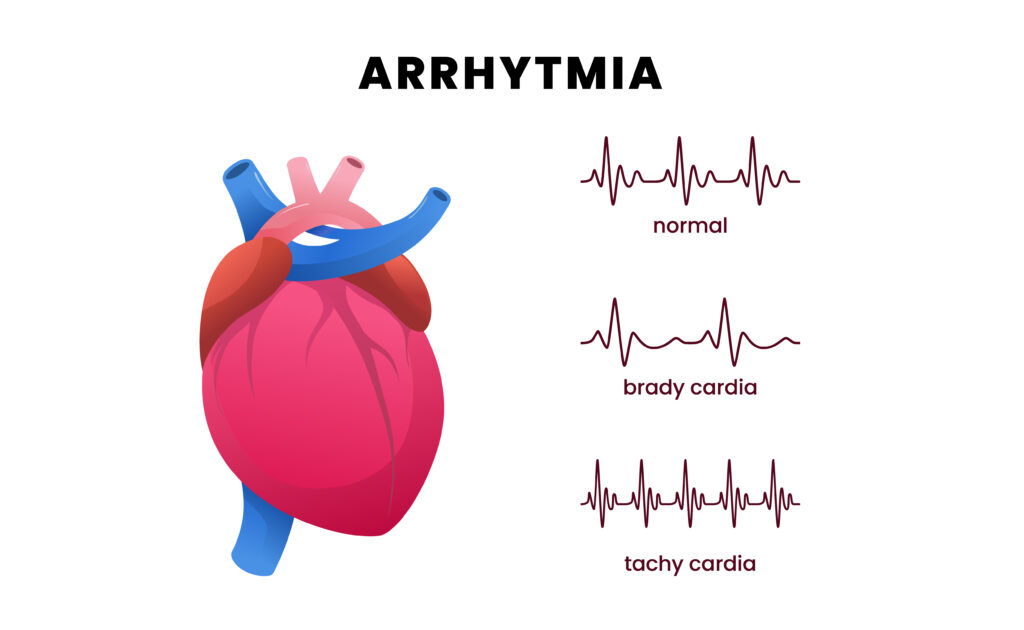
Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats that occur when the heart’s electrical signals don’t work properly, causing it to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly. This disruption in the heart’s rhythm can lead to various symptoms and complications, making it essential to understand the different types and treatment options.
Types of Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias can be categorized into several types based on their origin and characteristics:
Atrial Fibrillation (AF): AF is the most common type of arrhythmia, characterized by rapid and irregular beating of the heart’s upper chambers (atria). It increases the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other complications.
Bradycardia: Bradycardia occurs when the heart beats too slowly, typically fewer than 60 beats per minute. It can cause dizziness, fatigue, and fainting spells.
Tachycardia: Tachycardia refers to a rapid heartbeat, usually above 100 beats per minute. It can be further classified into supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and ventricular tachycardia (VT), depending on where the abnormal rhythm originates.
Premature Contractions: Premature contractions are extra, abnormal heartbeats that occur earlier than expected. They can manifest as premature atrial contractions (PACs) or premature ventricular contractions (PVCs).
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of arrhythmias vary depending on the type and severity but may include palpitations, chest discomfort, dizziness, shortness of breath, and fainting. Diagnosis often involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), and additional tests such as Holter monitoring or electrophysiological studies.
Treatment Options
Treatment for arrhythmias aims to control symptoms, prevent complications, and restore normal heart rhythm. Options include:
- Medications: Antiarrhythmic drugs can help regulate heart rhythm and prevent arrhythmia episodes.
- Cardioversion: This procedure involves restoring normal heart rhythm using electrical shocks or medications.
- Ablation: Catheter ablation involves destroying small areas of heart tissue responsible for generating abnormal electrical signals.
- Implantable Devices: Devices like pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) can help regulate heart rhythm and prevent dangerous arrhythmias.
